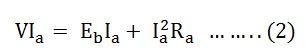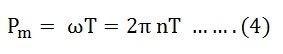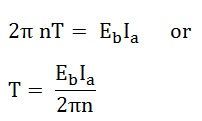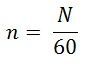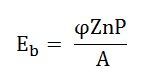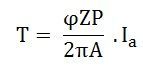To understand the torque equation, let us first understand the voltage equation of the DC motor.

Z = total number of armature conductors
A = number of parallel pathsi = current in each conductor = Ia/A
B = average flux density in Wb/m2
ϕ = flux per pole in Wb
P = number of poles
When the current-carrying current is placed in the magnetic field, a force is exerted or it which exerts turning moment or torque F x r. This torque is produced due to the electromagnetic effect, hence is called Electromagnetic torque.
The torque which is produced in the armature is not fully used at the shaft for doing the useful work. Some part of it gets lost due to mechanical losses. The torque which is used for doing useful work in known as the shaft torque.
Since,
Multiplying the equation (1) by Ia we get
Where,
VIa is the electrical power input to the armature.
I2aRa is the copper loss in the armature.
We know that,
Total electrical power supplied to the armature = Mechanical power developed by the armature + losses due to armature resistance
Now, the mechanical power developed by the armature is Pm,
Also, the mechanical power that rotates the armature can be given regarding torque T and speed n.
Where n is in revolution per seconds (rps) and T is in Newton-Meter.
Hence,
But, the back emf for dc motor is
Eb=ϕZNP60A
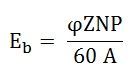
Where N is the speed in revolution per minute (rpm) and
Where n is the speed in (rps).
Therefore,
So, the torque equation is given as:
For a particular DC Motor, the number of poles (P) and the number of conductors per parallel path (Z/A) are constant.
Since, number of Poles (P) and number of the parallel paths (A) is constant,
∴ Ta ∝ ϕ Ia
(i) For a shunt motor, flux ϕ is practically constant
∴ Ta ∝ ϕ Ia
(ii) For a series motor, flux ϕ is directly proportional to armature current Ia provided magnetic saturation does not take place.
∴ Ta ∝ (Ia)2
As the armature rotates, a voltage is generated in its coils, which is called Generated EMF or Armature EMF, and is denoted by Eg.
Where,
Eg = Generated EMF
P = Number of poles of the machine
ϕ = Flux per pole in weber
Z = Total number of armature conductors
N = Speed of armature in revolution per minute (r.p.m)
A = Number of parallel paths in the armature winding
Also,
A = P ⋅ m
Where,
m = Multiplexity (simplex/duplex)
In wave winding, multiplexity is always 2 (two)
Therefore, A = 2
While in lap winding, there are two types:
- Simplex Lap winding: m = 1
∴ A = P
- Duplex Lap winding: m = 2
∴ A = 2P