3-Phase Induction Motor Braking
Following are the three main types of electrical braking of three phase induction motor
- Plugging/ Reverse voltage braking
- Regenerative induction motor braking
- Dynamic induction motor braking
1)Plugging Braking of Induction Motor :
- Plugging or counter-current braking: This is when the polarity of the supply voltage is reversed, causing the motor to run in the opposite direction and produce a braking torque. This method can stop the motor quickly, but it consumes a lot of power and may damage the motor. An external resistance is usually added to limit the current flow. You can learn more about this method from this source.
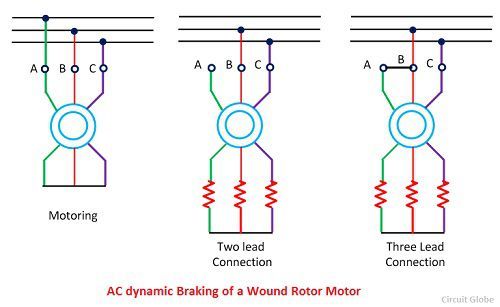
The dynamic braking is obtained when the motor is run on the single phase supply by disconnecting the one phase from the source and either leaving it open or connecting it with another phase. The two connections are respectively known as two and three lead connection.
3. Regenerative braking:
- Dynamic or rheostatic braking: This is when the motor is disconnected from the supply and connected to a braking resistor, causing the motor to act as a generator and dissipate the kinetic energy as heat in the resistor. This method can control the speed of the motor, but it wastes a lot of energy and requires a large resistor. You can learn more about this method from this source.
 This is when the motor operates as a generator and feeds the excess energy back to the supply system or a storage device. This method can save energy and reduce wear and tear on the motor, but it requires a variable frequency source and a special controller. This method can only work when the motor speed is higher than the synchronous speed. You can learn more about this method from this source.
This is when the motor operates as a generator and feeds the excess energy back to the supply system or a storage device. This method can save energy and reduce wear and tear on the motor, but it requires a variable frequency source and a special controller. This method can only work when the motor speed is higher than the synchronous speed. You can learn more about this method from this source.I hope this helps you understand the types of electric braking in electrical motors.
We know the power (input) of an induction motor is given as.
Pin = 3VIscosφs
Here, φs the phase angle between stator phase voltage V and the stator phase current Is. Now, for motoring operation φs < 90o and for braking operation φs > 90o. When the speed of the motor is more than the synchronous speed, relative speed between the motor conductors and air gap rotating field reverses, as a result the phase angle because greater than 90o and the power flow reverse and thus regenerative braking takes place.







